In today’s cloud-driven organizations, establishing an effective cloud governance framework is more than just a best practice—it’s a necessity.
As multicloud environments become the norm, managing the complexity of security, compliance, and cost efficiency is a central concern for both cloud architects and business leaders.
Effective cloud governance is a blend of culture and technology. It ensures that your organization not only adheres to regulatory requirements but also operates efficiently and optimally across cloud platforms such as AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure.

At DoiT, we recognize that successful governance isn’t solely about implementing the right tools. It’s about creating a unified framework that bridges teams, enforces policies, and enables visibility across your cloud landscape.
This comprehensive guide will explore what cloud governance is, why it’s essential, and how to build a framework that delivers on both security and cost efficiency, positioning your organization for long-term success.
What is cloud governance?
Cloud governance is a set of rules, policies, and processes designed to optimize the use of cloud resources while ensuring security, compliance, and cost management.
It serves as a framework to regulate the use of cloud services, helping organizations streamline operations across AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure, among others. Proper cloud governance involves managing cloud infrastructure, automating provisioning, enforcing access control, attributing finances to business segments, and mitigating security risks.
DoiT’s cloud optimization tools and expert services offer a holistic solution to tackle these common governance challenges while optimizing your cloud governance framework.
Why is cloud governance important?
Cloud governance is vital to maintain control over complex cloud environments, particularly in multicloud deployments where the use of cloud resources from different service providers must be carefully managed.
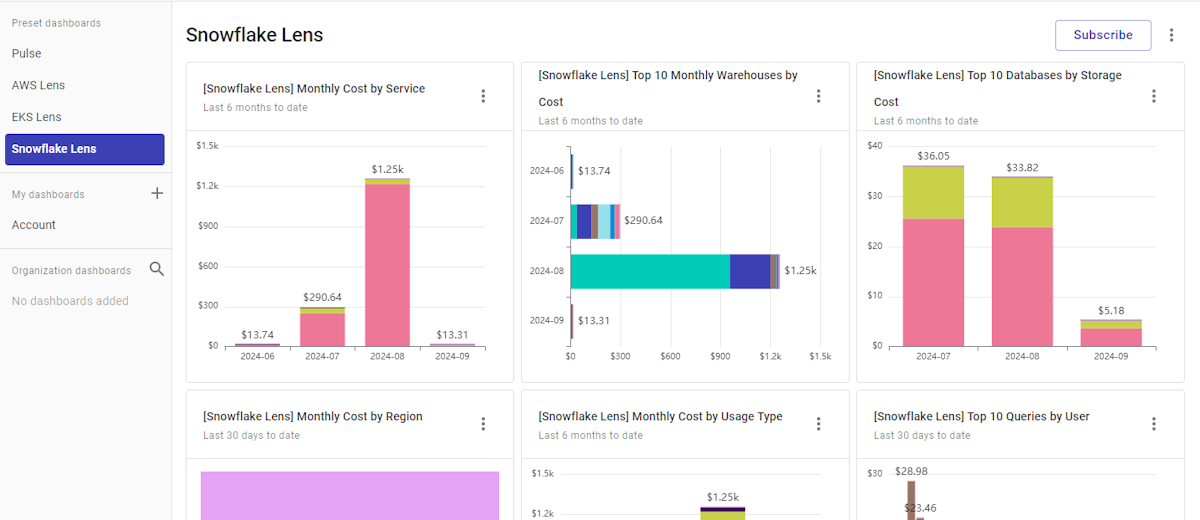
Platforms like DoiT Cloud Intelligence allow users to monitor costs across providers. (Source)
Effective cloud governance helps organizations manage and reduce cloud costs by optimizing cloud usage, monitoring cloud deployments, and setting financial guardrails to avoid unnecessary spending. By establishing a cloud governance strategy that includes regular audits and the use of monitoring tools, companies can streamline their cloud operations and attribute costs appropriately across an organization to better understand, analyze, and optimize across business departments.
For example, an organization may implement a governance policy that denies the deployment of an EC2 instance if proper tagging is not applied. This ensures that all resources are accounted for and can be tracked effectively for cost allocation and optimization.
Cloud governance is also critical in managing the security posture of an organization. With cloud services hosting sensitive data and applications, robust access control, provisioning, and IAM (Identity and Access Management) policies are necessary to mitigate cybersecurity risks and maintain data security. A governance framework ensures that security risks such as data breaches and unauthorized access are minimized by enforcing the proper use of cloud infrastructure and securing workflows across cloud systems.
IT teams need to detect anomalies, assess vulnerabilities, and ensure cloud security, especially when managing workloads distributed across multicloud environments, which presents significant challenges.
Therefore, monitoring and analytics solutions play a critical role in optimizing cloud operations within a governance model. These tools provide real-time visibility into cloud usage, enabling teams to effectively oversee cloud resources, manage governance policies, and ensure regulatory compliance.
DoiT Cloud Intelligence™, for example, helps centralize your cloud environment by gaining full visibility across all accounts so you can track usage, identify inefficiencies, and enforce policies efficiently from a single interface.
By leveraging monitoring and analytics, organizations can automate routine tasks, optimize performance, and secure cloud services across their entire cloud infrastructure.
5 key principles of cloud governance
To create a solid cloud governance framework, organizations need to focus on several core principles:
Cloud security
Cloud security is a critical pillar of any cloud governance strategy. It involves safeguarding cloud environments against vulnerabilities, unauthorized access, and data breaches.
Strong security measures—such as encryption, IAM policies, and regular security audits—help maintain a secure cloud infrastructure, ensuring that sensitive data and workloads are protected.
Compliance
Effective cloud governance ensures compliance with both internal policies and external regulatory standards. Organizations must enforce cloud governance policies that align with industry-specific regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and other certifications.
Regular compliance audits, automated monitoring, and governance guardrails are essential in keeping cloud operations in line with legal requirements.
Efficient cloud resource and cost management
Cloud governance frameworks should optimize cloud resource usage by automating provisioning, managing cloud costs, and ensuring that cloud services are used efficiently.
By monitoring cloud deployments and tracking cloud costs, organizations can identify opportunities to optimize and reduce unnecessary spending while ensuring workloads run smoothly. This results in improved operational efficiency and financial management across multicloud environments.
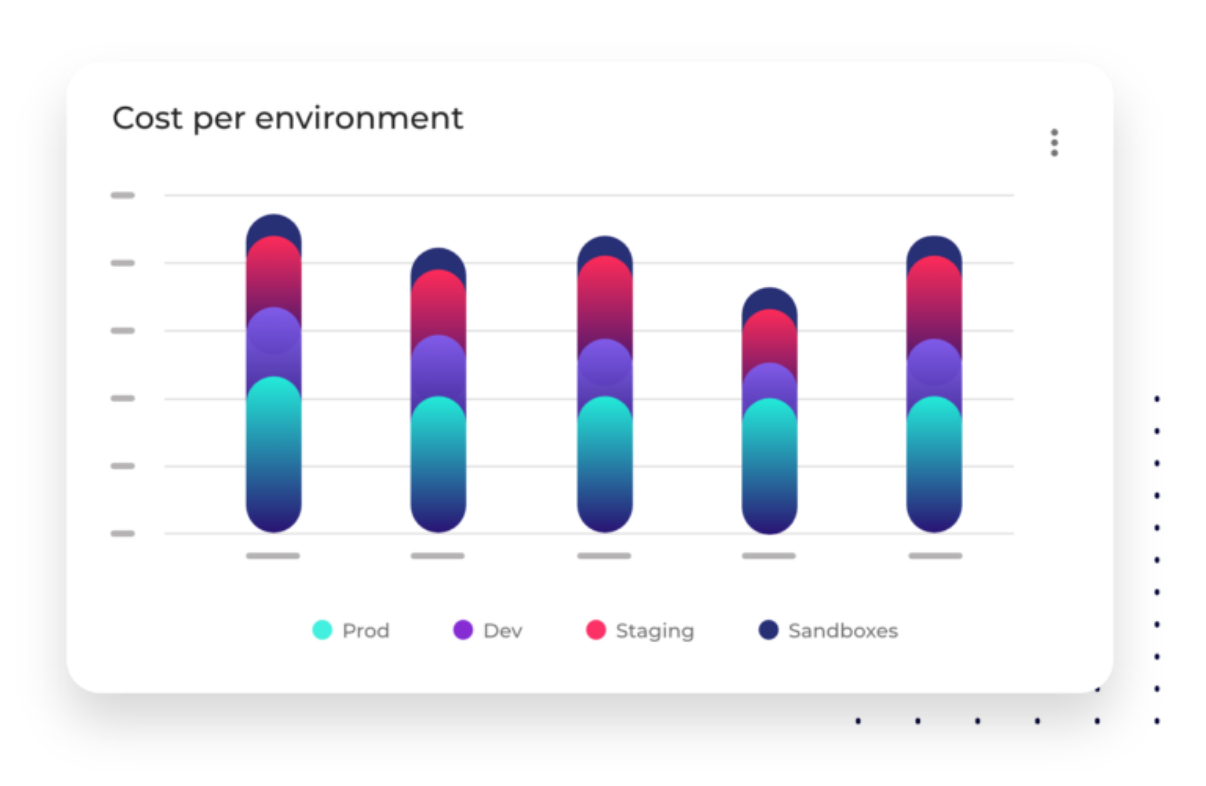
This mockup shows how DoiT’s cloud cost optimization solutions display cloud costs per environment. (Source)
DoiT’s cloud cost optimization services help you automate spend management, view and allocate cloud costs, and enhance your cost optimization strategy so you spend time and money on the workflows that matter most.
Alignment with business objectives
Cloud governance enables organizations to streamline cloud operations, ensuring that their cloud strategy is built around key business goals, such as scalability, security, and innovation.
By integrating governance with business objectives, companies can make better use of their cloud resources, accelerate growth, and maximize return on investment.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
IAM is essential for cloud governance as it ensures that the right people have access to the right cloud services and resources.
Each role—whether finance, engineering, or executive—plays a unique part in enforcing cloud governance policies. Engineers ensure that workloads are secure and optimized, finance teams focus on cost management and forecasting, and executives oversee governance models that align cloud usage with strategic business goals.
This role-based identity management ensures efficient cloud operations and reduces security risks across the organization.
Building a cloud governance framework
Creating an effective cloud governance framework requires a strategic approach that addresses both technical and cultural challenges. Follow these steps to develop a robust framework:
1. Assemble a cross-functional team
Include stakeholders from IT, security, finance, and compliance to ensure comprehensive governance. This diverse team will bring various perspectives, helping shape policies that align with organizational goals.
2. Conduct a thorough risk assessment
Identify potential vulnerabilities in your cloud environment and assess risks related to data security, regulatory compliance, and cost management. This assessment will inform the development of your governance policies.
3. Develop comprehensive policies
Create detailed policies covering:
- Identity and access management: Define user roles, permissions, and authentication processes.
- Data classification and protection: Establish protocols for classifying data based on sensitivity and applying appropriate security measures.
- Cost optimization: Set guidelines for resource allocation, usage monitoring, and cost reduction strategies.
- Compliance and regulatory requirements: Ensure adherence to industry standards and legal obligations.
- Security controls: Outline measures for threat detection, incident response, and ongoing security assessments.
4. Implement policies with a multilayered approach
Utilize a combination of native-cloud provider tools and third-party solutions for enhanced visibility and control. This approach can include:
Infrastructure layer: Employ infrastructure as code (IaC) for consistent, version-controlled deployments.
Platform layer: Implement centralized identity management and role-based access control (RBAC).
Application layer: Enforce DevSecOps practices and continuous compliance checks to maintain security throughout the development lifecycle.
5. Implement a comprehensive monitoring and observability stack
Ensure ongoing adherence to policies by integrating:
- Centralized logging and metrics collection for real-time insights
- Dashboards for monitoring security, compliance, and cost metrics
- Integration with Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) and Security Orchestration, Automation and Response (SOAR) platforms for enhanced threat detection and response.
6. Create a feedback loop and formal change management process
Establish workflows for approving significant changes and incorporate chaos engineering principles to test resilience. Regular tabletop exercises can validate incident response procedures, ensuring preparedness for potential security incidents.
As your cloud environment evolves, your governance framework needs to adapt. Investing in training and cloud governance services can help embed best practices across the organization.
Culturally, building an effective governance framework requires collaboration across departments. Regular cross-functional meetings can help set up guardrails and cloud governance policies, promoting consistent enforcement. Involving representatives from diverse departments, such as finance, security, and engineering, ensures comprehensive governance that aligns with organizational objectives.
Regular audits, real-time monitoring, and analytics (like DoiT DataHub) ensure ongoing compliance and provide insights for continuous improvement. Platforms like DoiT Cloud Intelligence™ can provide visibility into cloud operations, enabling you to track spending and detect inefficiencies.
When you follow the framework above, your org will experience the benefits of cloud governance, including enhanced security and strategic alignment. (Source)
3 Common cloud governance implementation challenges
Implementing cloud governance isn’t always smooth sailing. In fact, expect to encounter some rough waters when you’re just starting out.
Look out for these common roadblocks:
1. Shadow IT
Shadow IT—the use of unapproved cloud services and tools—can lead to security risks and unexpected cloud costs. Establishing strict access control and enforcing governance policies helps reduce shadow IT.
A great example of addressing shadow IT comes from One Data, a German software company and leader in data product management.
One Data eradicated hidden IT costs using cloud governance tools. With DoiT Flexsave™, the company achieved a 97.5% reduction in time spent preparing financial reports and saved 22% on its AWS compute instances.
By centralizing cloud account management and implementing financial governance measures, One Data regained control over unsanctioned cloud usage and streamlined its operations.
2. Scaling governance
As organizations grow, managing governance across multiple clouds and teams can become complex.
Each cloud service provider (CSP) has different mechanisms for enforcing governance policies, resulting in varied code implementations for each platform. Additionally, some organizations may operate multiple tenants within the same cloud, which complicates the ability to enforce policies systematically across those tenants.
Therefore, companies must establish a centralized management approach to ensure consistent governance practices while accommodating the unique requirements of each CSP.
By leveraging automation, organizations can reduce the risk of oversight and ensure that governance measures are consistently applied, even as their cloud landscapes evolve.
3. Cultural resistance
Teams may resist new cloud governance models, particularly when they perceive changes as restrictive.
Common challenges include overvaluing current practices and overestimating the negative impact of change. Established DevOps or cloud-native cultures might view governance as antithetical to their core principles of speed and autonomy.
Additionally, misalignment of incentives can arise when teams prioritize short-term productivity gains over long-term risk mitigation and compliance. Change management and ongoing training can ease this transition, ensuring that teams understand the benefits of governance measures.
Effective communication is crucial in these challenging situations. Organizations should clearly articulate the reasons behind governance changes and how they contribute to overall business objectives. Providing targeted training that emphasizes the importance of compliance and risk management can help foster a culture of shared responsibility.
5 best practices for implementing cloud governance
When building a cloud governance framework, following best practices ensures that your governance strategy remains effective and scalable.
1. Establish clear roles and responsibilities
Designate specific roles across departments such as finance, engineering, and IT to ensure accountability. For example, assign a cloud financial manager to oversee budget management and cloud cost optimization efforts.
A centralized team should manage role-based access control (RBAC), ensuring uniformity in access permissions across the organization. Application teams can submit requests through a formal ticket system, outlining specific use cases for roles and permissions, which helps maintain security while allowing teams to access the resources they need.
To prevent unauthorized access, align access rights with job functions, regularly review permissions to avoid privilege creep, and update roles as job functions evolve. Empower team leaders by providing the training and tools necessary to analyze their departments’ cloud usage, enabling them to make informed decisions about cloud spend and security policies.
This approach fosters a culture of ownership and accountability across departments, helping balance access management with operational efficiency.
2. Centralize visibility with a cloud management platform
Implement a unified platform like DoiT Cloud Intelligence™ to gain comprehensive visibility into all cloud accounts and services. Centralizing your cloud environments helps you track usage, identify inefficiencies, and enforce policies from a single interface.
3. Automate cost management and monitoring
Leverage tools like Flexsave™ and DoiT Anomaly Detection to automate cost-saving measures and monitor for cloud cost spikes. Automated governance is crucial in enforcing cost-related policies and ensuring that cloud expenditures remain aligned with budget forecasts.
Monitoring tools play a vital role in this process by ensuring that resources like CloudWatch metrics for EC2 instances are enabled and optimized. Utilizing AI for proactive threat detection and cost management can enhance monitoring efforts, creating alerts for potential anomalies in cloud usage.
Additionally, automated tagging policies are essential for accurate cost allocation, enabling organizations to track expenses by department or project and making it easier to identify areas for cost reduction.
4. Implement strong security and compliance standards
Enforce strict security measures across your cloud environments, including encryption, identity management, and regular security audits.
To enforce encryption, implement end-to-end encryption protocols for data at rest and in transit, ensuring that sensitive information is protected from unauthorized access.
For identity management, utilize multi-factor authentication (MFA) and centralized identity and access management systems to verify user identities and control access to cloud resources.
Regular security audits should be conducted to assess vulnerabilities, validate compliance with industry standards, and ensure that internal policies are adhered to, enabling proactive measures to prevent data breaches and maintain governance integrity.
5. Regularly review and update governance policies
Cloud environments evolve rapidly, so reviewing your governance framework every six to 12 months is essential to stay aligned with new services, regulations, and business objectives.
Key stakeholders, including IT, finance, legal, and department heads, should be involved to ensure cross-functional alignment.
Implement a formal process for proposing, reviewing, approving, and communicating policy changes, ensuring all updates are documented and accessible. Establish feedback loops by conducting user surveys and incorporating feedback from the teams that interact with cloud services daily.
This continuous improvement approach allows for real-time adjustments based on technological advances, shifting business priorities, and compliance updates.
Take control of your cloud
Effective cloud governance is essential for reducing costs, improving security, and ensuring your cloud infrastructure aligns with business goals. DoiT can help you build a cloud governance framework tailored to your organization’s needs.
Ready to implement cloud governance with DoiT? Book a discovery session today and start optimizing your cloud strategy.
[Book Your Call]