Enterprise Cloud Computing Solutions: Transforming Modern Businesses
You could very likely hit a few snags while leading a large organization through digital transformation or fine-tuning your existing complexities. Both come with their fair share of complexity.
For example, while cloud computing opens doors to innovation, you may need to tackle hybrid environment management and multi-cloud costs head-on. But the good news is that your existing technical debt from legacy systems can actually guide your modernization priorities, helping you make smarter choices about what to migrate and when. By embracing opportunities like containerization and automated operations, you're not just solving problems—you're positioning your organization to thrive.
Not sure where to start? Here we’ll cover the essentials of enterprise cloud computing to help you navigate your own strategy and avoid costly pitfalls.
What is enterprise cloud computing?
Enterprise cloud computing transforms IT resource delivery, rather than just moving your business operations to the cloud. It gives your organization on-demand access to computing resources and power, data storage, automation, and apps through internet-based services. Plus, it offers the scale and security that enterprise operations require.
Unlike smaller-scale cloud setups, enterprise cloud solutions handle complex workflows from mission-critical applications to data analytics platforms. They maintain security standards, ensuring regulatory compliance and high performance across global operations.
Gartner says that global enterprise spending on cloud services is projected to skyrocket, likely exceeding $675 billion in 2024. This surge reflects a fundamental shift in how enterprises operate. This means you need a strategic approach to cloud adoption and management, including cloud governance for control and compliance, FinOps for cost optimization, and workload optimization for peak performance and cost efficiency.
The 4 types of enterprise cloud computing models
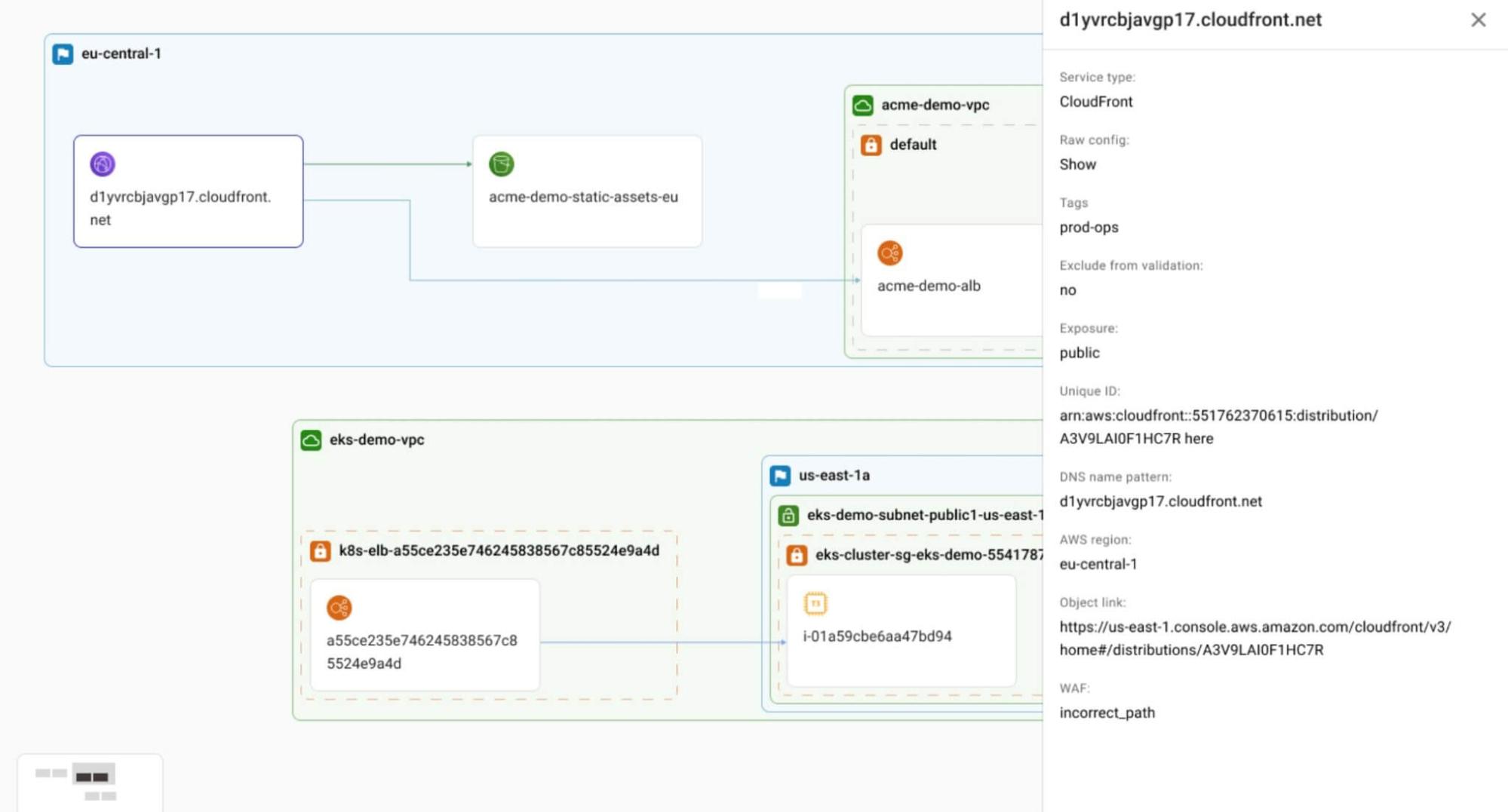
(Source)
Understanding the different cloud models can help you make informed decisions about your organization’s infrastructure. Each model offers distinct advantages and can be used independently or in a hybrid combination to meet specific business needs.
Public cloud
The public cloud offers services over the internet, with providers like AWS (Amazon Web Services), Google Cloud Platform, and Microsoft Azure managing the infrastructure. Benefits include:
- Rapid scalability without up-front infrastructure investment
- Pay-as-you-go pricing models
- Built-in redundancy and global reach
- Regular updates and new feature rollouts
However, some enterprises face challenges with public cloud implementations, particularly around data sovereignty and compliance requirements. For example, the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe requires organizations to maintain control of personal data, limiting data transfer to countries outside the European Economic Area.
Private cloud
Private cloud infrastructure is dedicated solely to your organization, either on-premises or hosted by a third party. Key advantages include:
- Complete control over infrastructure and security
- Customization to meet specific compliance requirements
- Predictable performance for critical applications
- Direct oversight of data location and management
Unlike public clouds, private clouds are often harder to scale because of limited physical infrastructure. You’ll need in-house expertise on-hand to handle maintenance, security updates, and hardware upgrades.
Private clouds also come with higher costs. Besides the upfront expenses, you’ll also need room in the budget for ongoing fees and increased maintenance responsibilities like upkeep and repairs. Managing a private cloud effectively requires IT staff who know virtualization, networking, and storage systems well.
Hybrid cloud
Hybrid cloud environments combine public and private clouds, allowing your organization to leverage the benefits of both. This model enables:
- Workload optimization across environments
- Cost-effective resource allocation
- Enhanced disaster recovery capabilities
- Flexibility to meet varying security requirements
If you’re in an industry like retail, this approach can be especially useful. It allows you to keep sensitive customer data secure in private clouds while using public cloud resources to handle holiday rushes or big sales events. As another example, in manufacturing, hybrid clouds are often used to process real-time IoT sensor data locally in private clouds for quick responses, while using public clouds for advanced analytics and long-term storage. As you can see, hybrid clouds can strike a great balance between security, performance, and scalability.
Multicloud
Many businesses also turn to multicloud strategies, using services from multiple providers to:
- Avoid vendor lock-in
- Optimize costs across providers
- Leverage best-of-breed services
- Enhance disaster recovery capabilities
Choosing the right cloud model for your business depends on three factors. First, consider your workload needs—performance, data processing, and any application dependencies. Then, think of your compliance and security requirements regarding data regulations and industry standards. Finally, look at up-front costs and long-term expenses to find the best cloud model for your organization’s needs.
What are the benefits of enterprise cloud computing?
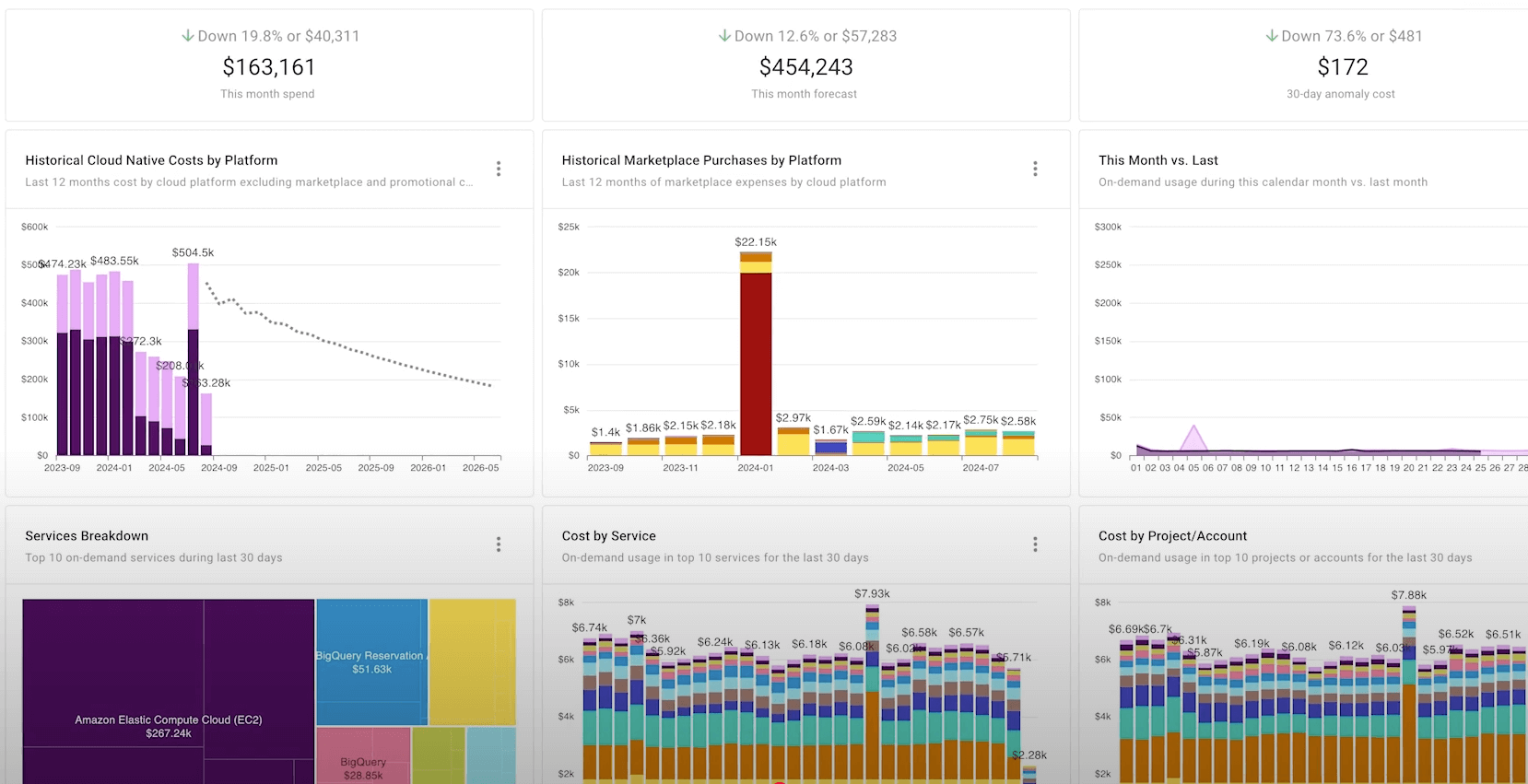
(Source)
Basic infrastructure savings are great, but the advantages of enterprise cloud computing also extend far beyond that. Your enterprise can use cloud capabilities to transform its operational efficiency, market responsiveness, and competitive advantage across multiple dimensions.
Scalability
In terms of scalability, your enterprise has the ability to adapt to market demands in real time, thanks to cloud computing services. Cloud technology allows your organization to scale its resources dynamically based on actual needs rather than relying on projected peaks.
For example, your company can quickly deploy new applications worldwide, increasing computing capacity during busy seasons. On the flip side, it can scale back during slower periods—all without the high costs and effort of maintaining excess capacity. This flexibility is beneficial especially if your business has variable workloads or seasonal operations.
Flexibility
Operational flexibility is another benefit of enterprise cloud computing, which means your organization can provide secure, consistent access to resources for distributed teams, no matter where they’re located. Beyond simply supporting remote work, cloud computing enables faster application deployment, seamless integration of new technologies, and the ability for you to adjust cloud resources as business needs change.
You can also experiment with new tools and services quickly without the need for large up-front investments. This approach encourages innovation while keeping risks manageable, offering your business a practical way to adapt and grow in a dynamic environment.
Cost efficiency
Enterprise cloud computing can be quite cost-effective, but only if you manage it carefully. By shifting from capital-intensive infrastructure investments to operational expenses, your company can better align costs with actual business value.
The pay-for-use model eliminates the need to maintain expensive excess capacity, while automated resource optimization helps reduce waste. Additionally, since cloud providers handle infrastructure upkeep and updates, enterprises enjoy reduced maintenance costs.
To get the most out of these cost savings, successful organizations often adopt FinOps practices, bringing finance, operations, and development teams together to keep an eye on and optimize cloud spending. Advanced cost-monitoring tools can track expenses across departments, spot unused resources, and predict future cloud costs. With the right FinOps setup and real-time cost tracking, companies can usually cut cloud spending by 20% to 30% while keeping everything running smoothly.
Collaboration
Cloud solutions—including real-time collaboration tools—are changing the way enterprise teams work together, making it easier to stay in touch across different locations and organizations. For instance, you’ve probably heard of or used the following:
- Cloud-based project management tools like Jira and Asana to keep track of tasks
- Real-time editing tools like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 that let teams work on documents together
- Communications tools like Slack and Microsoft Teams, which are ideal for chatting and video calls
- Shared code repositories like GitHub and GitLab that allow developers to collaborate
All of the above make it easy for teams to share resources, stay connected, and keep workflows running smoothly with simplified processes and more unified cloud platforms.
This capability is especially important for global enterprises managing complex projects across different locations and time zones. With the help of cloud solutions, your business can overcome common collaboration challenges and keep teams connected and productive.
Disaster recovery
Cloud adoption can also greatly improve disaster recovery and business continuity. Instead of maintaining expensive redundant data centers, enterprises can take advantage of cloud-based automated backup systems and geographically distributed infrastructure.
This approach reduces costs and also improves recovery capabilities by automating failover systems and reducing downtime risk. As a result, your business can maintain continuity during disruptions while keeping data secure and accessible to authorized users.
The top challenges in implementing cloud solutions
While the benefits of cloud computing are compelling, enterprises face several significant challenges when implementing cloud solutions. These require careful consideration and strategic planning to ensure successful cloud adoption and ongoing operations.
Security
Data security remains a top priority for enterprises adopting cloud solutions. This is especially true as organizations handle increasingly sensitive data across distributed environments. To navigate cloud security challenges, it’s essential to focus on a few specific areas:
- Data protection and compliance: Your organization needs robust strategies to protect data across multiple cloud environments while staying compliant with ever-changing global regulations. This includes implementing encryption, access controls, and regular audits to safeguard sensitive information.
- Identity and access management: Managing user identities in cloud environments can quickly become complex. A well-designed system balances strong security with ease of use so that only authorized individuals can access critical resources. Adopting Zero Trust security principles, where every access request is verified, and using identity management tools like Microsoft Azure AD or Okta make it easier to manage access with single sign-on across cloud services. These tools simplify adding or removing users, offering strong authentication controls like multi-factor authentication and conditional access based on things like user location, device status, and/or risk level.
- Threat detection and response: You can’t afford to do without comprehensive threat detection and response tools to monitor hybrid and multicloud environments. These tools should be able to identify and respond to increasingly sophisticated cybersecurity threats, working seamlessly across all platforms.
By addressing these core areas, your organization can create a more secure, compliant, and manageable cloud environment, reducing risk while enabling growth.
Integration
Integration is also one of the biggest challenges for enterprises transitioning to the cloud. Connecting cloud services to existing systems can reveal unexpected complexities, especially when you’re working with legacy systems that were not originally designed for cloud compatibility. For example, your data migration projects may encounter mismatched data formats or interdependencies between systems, or you may have concerns about maintaining business continuity during the migration process.
To address these challenges, your organization will need to carefully manage APIs to ensure secure and reliable connections between services while maintaining optimal performance. Service integration and orchestration across hybrid environments can also be complex, often requiring specialized tools and expertise. This process may demand significant time and resources, but with proper planning and the right support, you’ll be able to manage these hurdles effectively.
Spend management
Managing cloud spending is an ongoing challenge that requires careful attention and continuous improvement. The complex pricing structures of cloud services—covering various instance types, regions, and service levels—can make it difficult to accurately forecast costs and identify optimization opportunities.
Many organizations face challenges in resource optimization, needing to strike the right balance between performance and cost efficiency. Cost allocation across departments often adds another layer of complexity in cloud environments (especially when there’s a focus on FinOps), requiring the adoption of specialized tools and processes to ensure accurate tracking and accountability. Additionally, budget forecasting and control demand regular monitoring and adjustments, as usage patterns change and new services are introduced.
5 best practices for enterprise cloud adoption
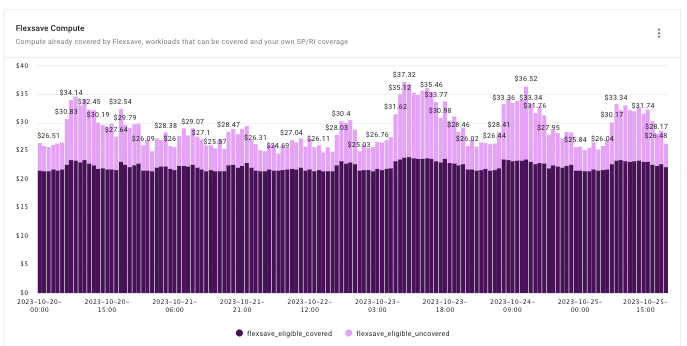
(Source)
Success in enterprise cloud computing requires a strategic approach focused on achieving specific business outcomes. This means aligning cloud solutions with organizational goals, optimizing workflows, ensuring scalability, and maximizing efficiency while reducing costs.
Here are some best practices for successful enterprise cloud adoption:
1. Align with business needs
Start by aligning your cloud initiatives with your business goals. Talk to stakeholders from different teams to understand their needs and challenges. Identify specific use cases where cloud adoption adds value, such as speeding up application deployment, enhancing customer experience, and enabling data-driven decisions. When prioritizing key workloads, look at dependencies, performance needs, and their overall business impact. Ensure your success metrics are measurable and tied to real results, such as faster time-to-market or higher customer satisfaction. These insights can set a solid foundation and shape your cloud strategy, including timelines, resource planning, and risk management.
2. Choose the right model
Choose the right cloud model by listing your applications and data, and take note of their needs—performance, security, compliance, and integration. Customer-facing apps with unpredictable traffic might work best on public cloud, while sensitive financial systems could require private cloud infrastructure. Don’t skip over compliance—some regulations might dictate where your data needs to live or what security controls are necessary. Be sure to weigh both immediate and long-term costs, including operational expenses and potential savings. And don’t forget to plan for future growth, keeping in mind things like data size, user demand, and possible expansion into other locations.
3. Develop a migration strategy
Create a clear migration roadmap by breaking the process into more manageable steps. Start with less critical applications to fine-tune your approach, using cloud migration assessment tools to evaluate dependencies and identify potential risks. Prioritize which applications to migrate based on their business impact, technical complexity, and interdependencies, and include thorough testing (performance checks, security validation, and user acceptance testing). Also, have solid contingency plans in place for each phase, including rollback options and measures in case things don’t go as planned.
4. Implement security and compliance
Build security into your cloud infrastructure from the start. A risk assessment can pinpoint potential vulnerabilities and compliance so you know what to tackle first. Use automation and infrastructure as code to set up security controls—this reduces human error and ensures consistency. Take advantage of cloud security posture management tools to watch for misconfigurations and compliance issues. The goal is to keep your security strong with automated compliance checks, regular penetration tests, and routine security reviews.
5. Optimize costs
Take control of cloud spending with cost management strategies like automated monitoring, cost optimization tools, and clear resource tagging. Set up policies to shut down unused resources, right-size your instances, and make the most of reserved instances or savings plans for predictable workloads. Regularly review your architecture to keep it cost-efficient, use auto-scaling, and consider containerization or serverless options. Build a FinOps culture by bringing finance, engineering, and operations teams together to track spending and key metrics like cost per customer or transaction, so you can get the most out of your cloud investment.
Maximize your enterprise cloud investment with DoiT
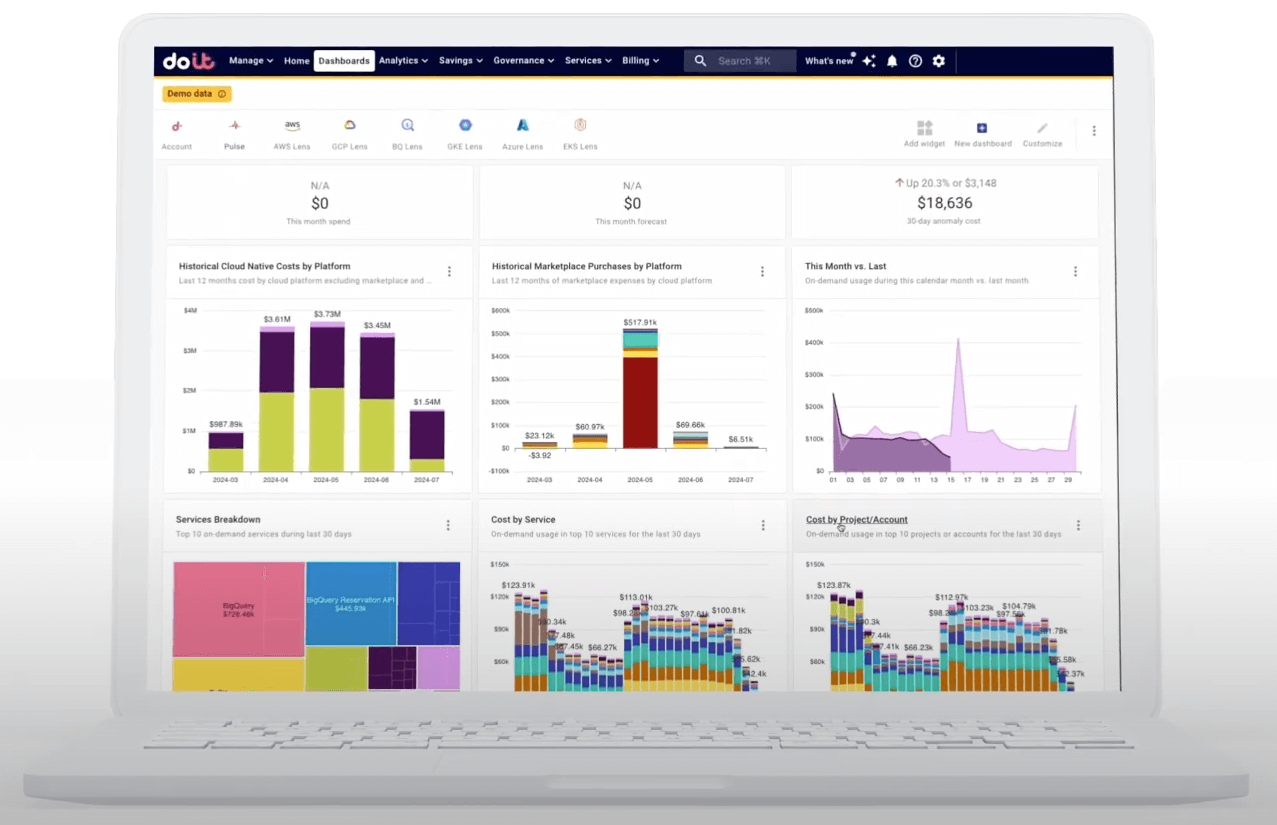
(Source)
Optimizing your enterprise cloud infrastructure requires expertise and the right tools. DoiT’s cloud management solutions can help you navigate these challenges while maximizing both your cloud investment and its functionality.
DoiT’s platform offers unified visibility across multiple cloud service providers, enabling teams to monitor and optimize their entire cloud ecosystem from a single dashboard. Our platform tackles enterprise challenges with smart tools for cost management, performance boosting, and cloud governance. We reduce cloud waste by analyzing your spending, ensure smooth app performance, and automate compliance to stay secure and control costs.
Ready to take your cloud operations to the next level? Our expert team works closely with you to identify opportunities for savings and streamline your IT infrastructure, so you can focus on innovation and growth.
Contact us today to learn more about how we can support your business with tailored cloud solutions.